[Arduino Uno] 4bits LED binary counter
Created:
Updated:
circuit
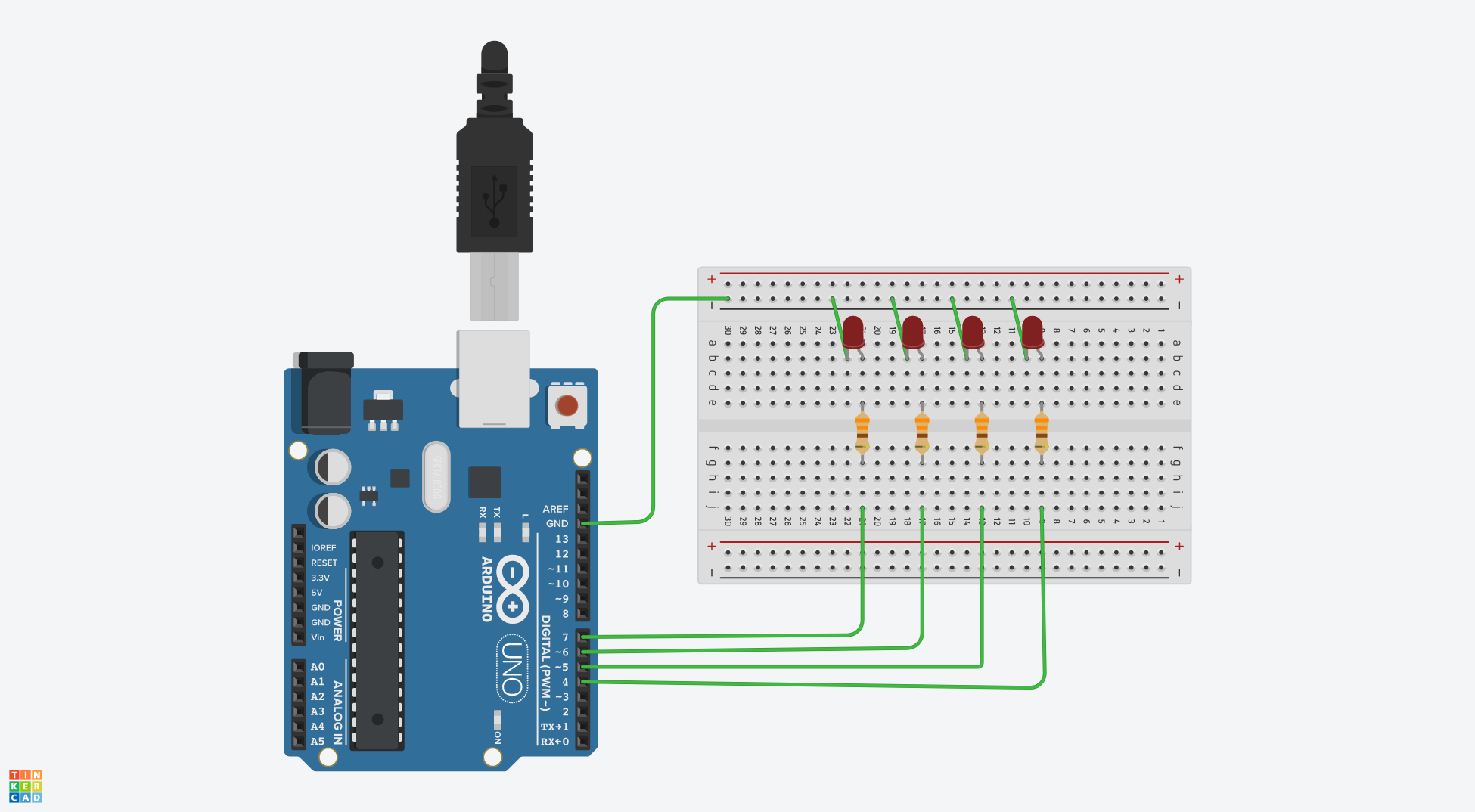
The circuit below is a 4bits binary counter with 4 red LEDs. The exact characteristics of the LED should be checked in its datasheet. It is assumed here that it is 2.0V forward voltage, at 20mA current. That is, the resistor value must be determined not to exceed 20mA at the maximum. Otherwise, the LED may be damaged and burn out. In this example, let’s calculate a current of about 10mA. The resistance value can be calculated as follows according to Ohm’s law. Since the high output voltage of digital 4, 5, 6 and 7 ports of Arduino Uno is about 5v, and the forward voltage of LED is 2v. So the formula is :
$I = \frac{V}{R} = 0.01A = \frac{(5V-2V)}{R} $
$R = \frac{3V}{0.01A} = 300 \Omega $
So, if we choose a resistance of about 300 ohms, a current of about 10mA draws. In this example, 330 ohms was used. Arduino Uno’s ports 4, 5, 6 and 7 are connected to BIT0, BIT1, BIT2 and BIT3, respectively, and when the ports output HIGH, the LED are designed to turn on.(common-cathod)
code
In the source code, “count++” is performed every second, and the count value is bit-operated to output HIGH in case of 1, and LOW in case of 0.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#define BIT0 4
#define BIT1 5
#define BIT2 6
#define BIT3 7
unsigned int count = 0;
void setup()
{
pinMode(BIT0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIT1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIT2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIT3, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(BIT0, (count & 0x1));
digitalWrite(BIT1, ((count >> 1) & 0x1));
digitalWrite(BIT2, ((count >> 2) & 0x1));
digitalWrite(BIT3, ((count >> 3) & 0x1));
delay(1000); //Wait for 1000 milisecond(s)
count++;
}
Leave a comment